Aevel经济微观部分AS阶段重要概念汇总
在Alevel经济这门科目当中,很多同学都会基础到大量的概念问题,本期我们给大家汇总了Alevel经济微观部分AS阶段的一些重要概念,大家可以参考一下,也可以收藏哦!另外这个各个不同课程体系的学生都可以看一看。
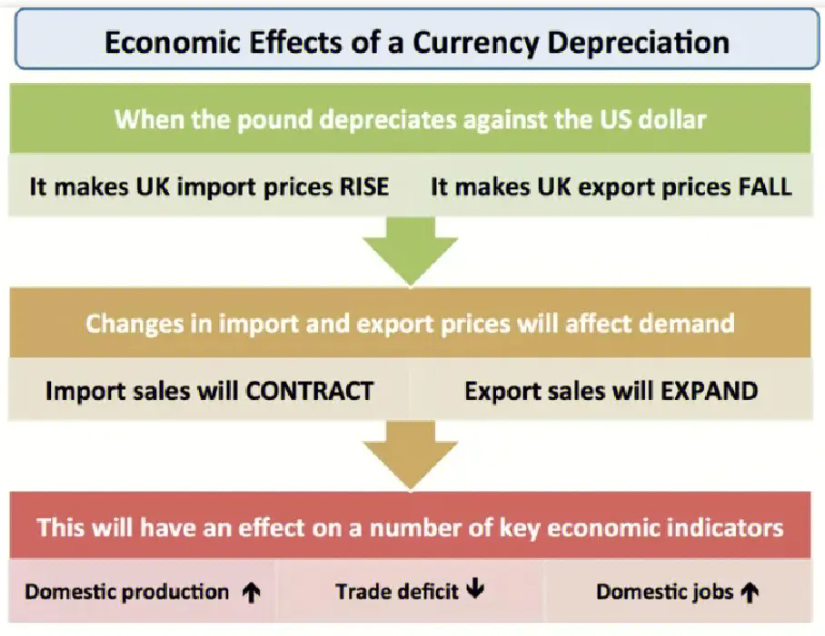
Micoeconomics definitions
Ad Valorem Tax: An indirect tax, levied as a percentage of the price of a good.
Asymmetric Information: Agents have asymmetric information when some agents have more information than others. Buffer Stock Scheme: Used by the government to reduce price fluctuations by buying and selling a commodity to ensure price remains within a band.
Capital. A factor of production: Man-made aids used by labour in the production process. Capital includes machines, buildings, computers, telecommunications, roads etc.
Command Economy: In a command economy the government directs resource allocation.
Complements: Complements are goods that are bought (usually) to be used together, they have a negative XED.
Consumer Surplus: Consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing (and able) to pay and what they actually pay. Consumer surplus is the area between the demand curve and the market price.
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand: XED measures the responsiveness of demand for good X to a change in price of good Y.
Demand: Demand is the quantity of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at the market price in a given time period.
Demerit Good: A demerit good has costs for the consumer who buys it but the consumer may be unaware of its full costs. A demerit good is over-consumed due to asymmetric information.
Direct Tax: A direct tax is a lump-sum tax on income.
Division of Labour: Refers to labour specialization in the production process, where workers take on specific roles.
Enterprise: A factor of production. Risk-taking by an individual or group who combine the other factors of production in search of profit.
Excess Demand: Excess demand occurs when demand is greater than supply.
Excess Supply: Excess supply occurs when supply is greater than demand.
External Benefit: An external benefit is an unpaid for benefit enjoyed by 3rd parties not directly involved in a market transaction.
External Cost: An external cost is an uncompensated cost imposed on 3rd parties not directly involved in a market transaction.
Factors of Production: The factors of production are the inputs used in the production process to produce output.
They include land, labour, capital and enterprise.
Free Market Economy: A free market economy is an economic system which resolves the basic economic problem through the price mechanism.
Geographical Mobility of Labour: Refers to the ability of labour to move between different areas to find a job. For example, moving from Manchester to London to find work.
Government Failure: When government intervention distorts the market and causes inefficiency.
Income Elasticity of Demand: YED measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in income.
Indirect Tax: An indirect tax is a tax levied on the sale of goods.
Inferior Good. As income rises, demand falls. An inferior good has a YED<0.
Labour:A factor of production. Labour is the worker in the production process. Labour can be skilled or unskilled. Land:A factor of production. Land is all the natural resources on the planet. Land includes oil, forests, soil, fish etc.
Long-Run:All the factors of production are variable in the long-run.
Luxury:As income rises, quantity demanded rises more proportionally. A luxury has a YED>0.
Market Failure:Market failure occurs when the price mechanism allocates resources inefficiently. There is a welfare loss. Market failure could occur due to: Monopoly, Public Goods, Externalities or Asymmetric Information.
Maximum Price:A maximum price is a price ceiling, the market price cannot rise above it.
Merit Good:A merit good has benefits for the consumer who buys it but the consumer may be unaware of its full benefits. A merit good is under-consumed due to asymmetric information.
Minimum Price:A minimum price is a price floor, the market price cannot fall below it.
Minimum Wage:The minimum wage is the legal minimum hourly rate of pay.
Mixed Economy:A mixed economy is an economic system which allocates resources partly by the price mechanism and partly by the government.
Necessity:As income rises, quantity demanded rises less proportionally. A necessity has a 0 Non-Renewable Resources:Non-renewable resources are ones whose stock level decreases over time as it is consumed for example, fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal) and commodities (gold and aluminium). Recycling and developing alternative resources helps reduce the rate of decline of non-renewables. Normal Good: As income rises, demand rises. A norm al good has a YED>0. Normative Statement: A normative statement is a value judgement or view. It usually contains the words ought or should. Occupational Mobility of Labour: Refers to the ability of labour to move between different types of jobs. For example, footballer to university lecturer. Opportunity Cost: Opportunity cost is the next best alternative foregone. Positive Statement: A positive statement can be proved right or wrong by real world data. Price Mechanism: The price mechanism refers to the way in which demand and supply interact to change prices and allocate resources. Price Elasticity of Demand: PED measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. Price Elasticity of Supply. PES measures the responsiveness of supply to a change in price. Private Benefits: Benefits enjoyed by a 1st or 2nd party directly involved in a market transaction. Private Costs: Costs incurred by a 1st or 2nd party directly involved in a market transaction. Private Goods: Private goods are excludable and rival. Excludable means the good can only be used by the consumer who buys it. Rival means the consumption by one individual reduces the amount available for others to consume. Producer Surplus: Producer surplus is the difference between the price producers are willing (and able) to supply at and what they actually receive. Producer surplus is the area between the market price and the supply curve. Production Possibility Frontier (curve): A PPF(PPC) shows all the different combination of goods an economy can produce if all resources are fully and efficiently employed. Public Goods: Public goods are non-rival and non-excludable. Non-rival means the consumption by one individual does not reduce the amount available for others to consume. Non-excludable means anyone can use the good even if they do not pay for it. Renewable Resources: Renewable resources are ones whose stock levels can be maintained over a period of time for example, oxygen, water, timber, soil, solar energy and wind power. Biological or natural processes replenish these resources over time for example, trees grow. Renewable resources will run out if they are consumed quicker than they are replenished for example, a forest must be managed to avoid deforestation. Short-Run: The short-run is that period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed (usually land and/or capital). Specialisation: A factor of production is devoted to a specific role in the production process. Specific Tax: An indirect tax. A specific tax is levied as a fixed amount per unit of a good bought/sold. For example, a tax of £10 per unit. Subsidy: A grant given by the government to producers to lower costs and increase production. Substitutes: Substitutes are alternative or replacement goods that satisfy similar wants, they have a positive XED. Supply: Supply is the quantity supplied of a good or service that a producer is willing and able to sell at the market price for a given time period. Sustainable Resources: Sustainable resources are a type of renewable resource. Sustainable resources are ones that are used at the same (or slower) speed than it is renewed. A forest is a renewable resource but it is only a sustainable resource if it survives over time despite activities like logging or farming. A forest that is chopped down is no longer a sustainable resource. Symmetric Information: All agents have the same information. Welfare Loss: A loss to society due to market failure. 以上就是关于Aevel经济微观部分AS阶段重要概念的汇总,对于这些知识概念有不清楚的地方,记得及时咨询我们的Aevel经济课程辅导老师哦~
当前文章链接:
凡来源标注“考而思”均为考而思原创文章,版权均属考而思教育所有,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,否则追究法律责任
上一篇:
下一篇:
免费获得学习规划方案
已有 2563 位留学生获得学习规划方案
马上领取规划
*已对您的信息加密,保障信息安全。